

The phenomenon of image formation through reflection is fascinating and plays a crucial role in our daily lives. Whether we look in a mirror, observe objects in water bodies, or even catch a glimpse of ourselves in a shiny surface, reflection helps create these images.We will explore the concept of image formation by reflection, delve into the different types of images formed, and understand the distinction between real and virtual images. So, let's embark on this captivating journey of optics and reflection!
What is Image Formation?
Image formation refers to the process of creating a representation of an object through the reflection of light. When light rays from an object strike a surface, they undergo reflection and form an image. The surface could be a mirror, a shiny metallic object, or even the surface of water. The reflection process allows us to perceive the image of an object, enabling us to see ourselves and the world around us.
Types of Images Formed
a) Real Images:

Real images are formed when light rays converge at a particular point after reflecting from a surface. These images can be projected onto a screen and are formed when the reflected light rays actually meet. Concave mirrors and converging lenses are responsible for the formation of real images. They possess certain characteristics: they are always inverted, can be obtained on a screen, and are generally larger or smaller than the object depending on the distance between the object and the reflecting surface.
b) Virtual Images:
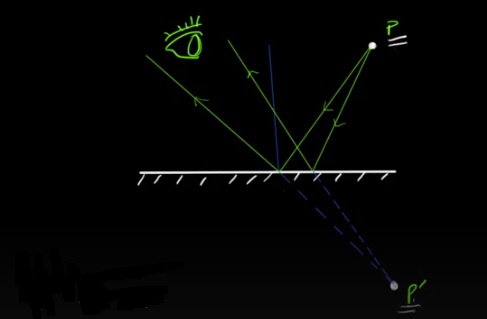
Virtual images are formed when the light rays appear to diverge from a specific point behind the reflecting surface. These images cannot be projected onto a screen and are formed when the reflected light rays appear to meet. Virtual images are formed by convex mirrors and diverging lenses. They possess distinct characteristics: they are always erect (upright), cannot be obtained on a screen, and are usually smaller than the object.
Distinction between real and virtual images
|
Real Image |
Virtual Image |
|
a) Real images are formed when light rays converge at a specific point after reflecting from a surface. |
a) Virtual images are formed when light rays appear to diverge from a specific point behind the reflecting surface. |
|
b) This convergence of light rays creates an image that can be projected onto a screen or captured on a photographic surface. |
b) These images cannot be projected onto a screen or captured on a photographic surface. |
|
c) The point from which the light rays appear to originate is known as the focus or focal point. |
c) The point from which the light rays appear to originate is known as the virtual focus or virtual focal point. |
|
d) In the case of real images, the light rays actually meet or converge, forming an image that can be projected and captured. |
d) Virtual images are formed by convex mirrors and diverging lenses. |
|
e) Real images are formed by concave mirrors and converging lenses. |
e) Unlike real images, virtual images are not formed by the actual convergence of light rays, but rather by their apparent divergence. |
Difference between Real and Virtual Images
a) Formation Process:
Real images are formed when actual convergence of light rays occurs, whereas virtual images are formed when light rays appear to diverge.
b) Projection:
Real images can be projected onto a screen, whereas virtual images cannot be projected and can only be seen when looking through the reflecting surface.
c) Orientation:
Real images are always inverted (upside down), while virtual images are always erect (upright).
d) Location:
Real images are formed in front of the reflecting surface, while virtual images are formed behind the reflecting surface.
e) Size:
The size of a real image can be larger or smaller than the object, depending on the distance between the object and the reflecting surface. Virtual images are usually smaller in size compared to the object.
f) Interaction with Light:
Real images interact with light, meaning they can be focused onto a screen, photographed, or projected. On the other hand, virtual images do not interact with light, making them non-projectable.
The formation of images by reflection is a fascinating concept that surrounds us in our everyday lives. Understanding the different types of images, namely real and virtual images, allows us to comprehend how light interacts with surfaces and how our eyes perceive the world around us. The ability to differentiate between real and virtual images provides us with valuable insights into optics and helps explain various phenomena we encounter daily. So, the next time you look in a mirror or observe a reflection, take a moment to appreciate the intricate process that forms these captivating images!
