The long form of the periodic table is an improved layout of elements that highlights the repeating patterns in their properties. It follows the Modern Periodic Law, which states: "The chemical properties of elements repeat at regular intervals when arranged in order of increasing atomic numbers."
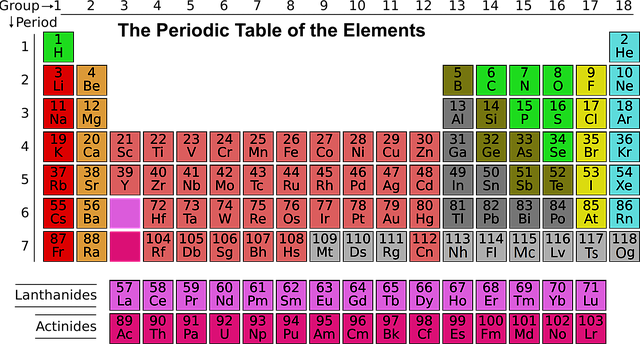
Figure: The modern long form of the periodic table showing groups and periods.
This form of the periodic table arranges the elements in increasing order of atomic numbers and groups them in such a way that elements with similar chemical and physical properties fall into the same vertical columns. The long form is more accurate than earlier versions and is widely used in schools, laboratories, and scientific research.
The periodic table is made up of 18 vertical columns, called groups, and 7 horizontal rows, known as periods. It contains a total of 118 known elements as of now, classified as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids.
In the periodic table, groups refer to the vertical columns. There are a total of 18 such columns. Elements that belong to the same group exhibit similar chemical characteristics due to having an identical number of electrons in their outermost shell (valence electrons).
Key Features of Groups:
Periods are the horizontal rows found in the periodic table. There are a total of 7 periods. All elements in the same period have an equal number of electron shells. However, their properties show a gradual variation across the period from left to right because the positive charge on the nucleus increases.
Key Features of Periods:
The long form of the periodic table is a scientifically accurate and organized method of classifying elements. By understanding the roles of groups and periods, students can better grasp the trends and behaviors of elements, which is essential for mastering chemistry.