In the world of optics, lenses play a fundamental role in shaping our vision and understanding of the physical world. One important type of lens is the concave lens.
Concave Lenses:
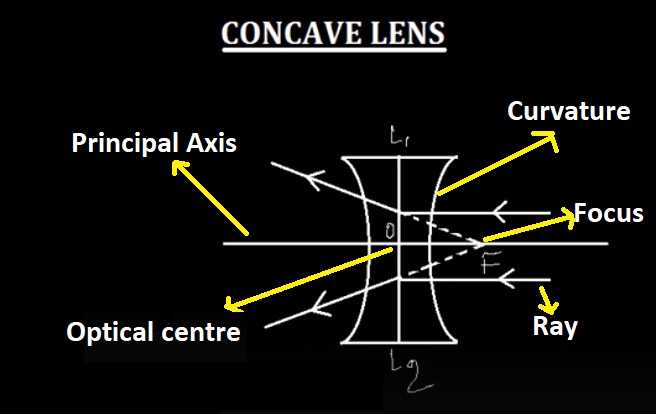
A concave lens, also known as a diverging lens, is characterized by its thinner center and thicker edges. This shape allows the lens to disperse light rays that pass through it, causing them to diverge. Concave lenses are designed to correct nearsightedness (myopia) and are often used in eyeglasses or contact lenses for individuals with this condition. Understanding the concept of concave lenses begins with the principal axis.
Principal Axis and Curvature of Concave Lenses:
The principal axis is an imaginary line passing through the center of a lens, perpendicular to its surfaces. In the case of concave lenses, the principal axis coincides with the lens's symmetry axis. This axis is crucial for understanding how concave lenses function. When parallel rays of light strike a concave lens, they are refracted and diverge away from the principal axis. The spreading of rays happens because of the curved shape of the lens.
The curvature of a lens refers to the degree of curvature of its surfaces. In the case of a concave lens, both surfaces are curved outward. The curvature is usually uniform across the lens. The extent of curvature affects the refractive power of the lens. A highly curved concave lens has a greater refractive power, dispersing light rays to a larger extent. This property allows concave lenses to focus light in a specific manner.
The Focus of a Concave Lens:
The focus of a lens is the point where parallel rays of light converge or appear to converge after passing through the lens. In the case of a concave lens, the focus is referred to as the virtual focus. Unlike convex lenses, which have a real focus, concave lenses disperse light rays and cannot produce a real focus.
A concave lens causes parallel light rays to spread outward, away from the principal axis. By tracing these diverging rays backward, they seem to originate from a point on the principal axis. This point is known as the virtual focal point of the concave lens. It is essential to understand that the virtual focus lies on the same side as the object being observed. In other words, the virtual focus is always on the same side as the incident light.
The virtual focus of a concave lens has several important implications. For instance, when an object is placed at the virtual focus distance from the lens, the emerging rays appear parallel after passing through the lens. Consequently, an observer looking through a concave lens at an object placed at the virtual focus sees a clear image with minimal distortion.
Optical Center in Concave Lenses:
The optical center, in the context of concave lenses, refers to a fixed point within the lens where incident light rays pass through without deviation or refraction. This point remains unaffected by the passage of light and is typically located at the geometric center of the concave lens. It coincides with the intersection of the principal axis and the symmetry axis of the lens. Understanding the optical center's properties and location is crucial for comprehending how concave lenses interact with light.
Focal Length:
The focal length of a lens refers to the distance between the lens and its focal point. It is denoted by the symbol "f" and is a crucial parameter that describes the lens's ability to converge or diverge light. For concave lenses, the focal length is negative, indicating their diverging nature. The focal length of a concave lens determines the degree of divergence and the resulting behavior of light rays passing through it.
Concave lenses are remarkable optical devices that allow us to correct nearsightedness and observe objects with enhanced clarity. By understanding the principal axis, curvature, and focus of a concave lens, we can appreciate the intricate workings of this diverging lens. The virtual focus, unique to concave lenses, offers valuable insight into their optical properties and applications. Whether it is correcting vision or exploring the mysteries of light, the concept of concave lenses is an integral part of the