Understanding Heat Conduction:
Heat conduction is the process by which heat energy is transferred through direct contact between objects or substances. It occurs when two objects at different temperatures come into contact with each other, resulting in the transfer of thermal energy from the hotter object to the cooler one. The primary driving force behind heat conduction is the temperature difference between the objects.
Factors Affecting Heat Conduction:
The rate of heat conduction is influenced by several factors.
Thermal conductivity: Different materials have varying abilities to conduct heat. Materials with high thermal conductivity, such as metals like copper and aluminum, facilitate efficient heat transfer. On the other hand, insulating materials like wood or rubber have low thermal conductivity, impeding heat flow.
Surface area: The larger the contact area between objects, the greater the potential for heat transfer. Increased surface area allows for more direct contact and, consequently, more effective heat conduction.
Temperature gradient: The temperature difference between two objects directly impacts the rate of heat conduction. The greater the temperature difference, the faster the heat transfer occurs.
When a solid material is heated externally by a burner, a fascinating process called heat conduction takes place. Let's explore how this phenomenon occurs.
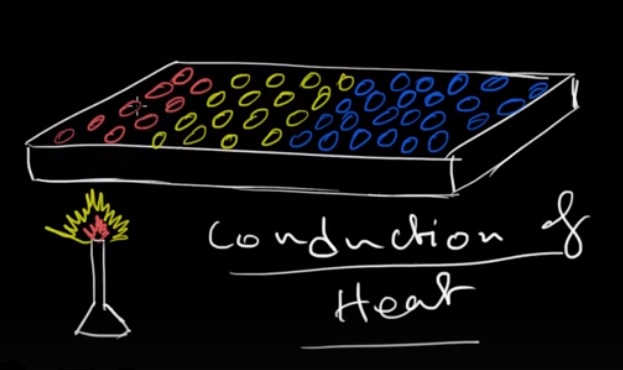
The burner, typically a flame or a heat source, is applied to the surface of the solid material. As the burner releases heat energy, it transfers this energy to the solid material through direct contact. The high temperature of the burner causes the particles near the surface of the solid material to vibrate vigorously, gaining kinetic energy.
These highly energetic particles then collide with neighboring particles, transferring some of their kinetic energy. This collision process continues throughout the solid material, causing a chain reaction of particle interactions. As a result, the kinetic energy is gradually transferred from the heated surface to the deeper layers of the solid material.
The transfer of heat energy in this manner is known as heat conduction. It occurs due to the temperature difference between the burner and the solid material. The principle behind heat conduction is that heat always flows from regions of higher temperature to regions of lower temperature.
The rate of heat conduction depends on several factors. One crucial factor is the thermal conductivity of the solid material. The ability of materials to conduct heat varies across different substances. Metals, such as copper or aluminum, are excellent conductors of heat and facilitate efficient heat transfer. In contrast, materials like wood or rubber have lower thermal conductivity, which means they conduct heat more slowly.
Another factor influencing heat conduction is the thickness of the solid material. Thicker materials require more time for the heat to travel through them, resulting in slower heat conduction.
Overall, when a solid material is heated externally by a burner, heat conduction allows the transfer of thermal energy from the hot surface to the interior of the material. This process plays a significant role in various applications, such as cooking, industrial processes, and even everyday situations like heating utensils or objects. Heat conduction helps distribute the heat evenly, ensuring that the entire material reaches a uniform temperature.