Understanding Light:
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that enables us to see the world around us. It is composed of tiny particles called photons, which travel in straight lines known as light rays. When light rays encounter an object, they interact with its surface, giving rise to various optical phenomena.
Light Ray: The Path of Light:
A light ray refers to the path along which light travels. It is represented as a straight line to simplify the study of light and its behavior. Light rays can pass through transparent materials like air or glass, be absorbed by opaque objects, or bounce off reflective surfaces.
Reflection: Revealing the Visible World:
Reflection is the process by which light rays bounce off the surface of an object and change their direction. This phenomenon is responsible for making objects visible to our eyes. When light hits a surface, it interacts with the atoms or molecules of the material, causing the light rays to reflect in different directions.
Angle of Incidence and Angle of Reflection:
The angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are vital concepts in the study of reflection. Let's explore what these angles represent:
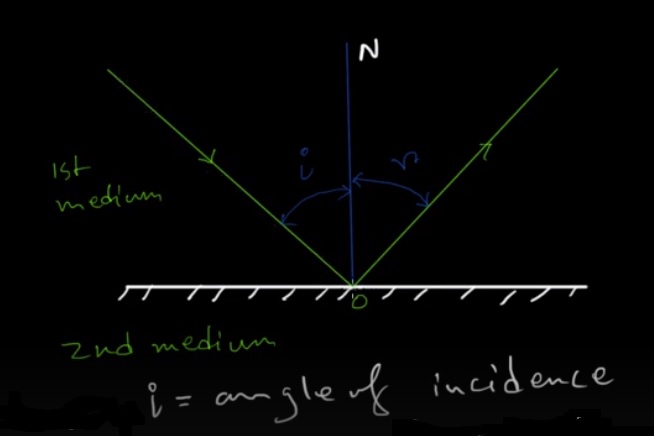
Angle of Incidence: The angle of incidence is the angle formed between the incoming light ray and the perpendicular line, known as the normal, which is drawn at the point where the light ray intersects the surface. It is denoted by the symbol \(\theta_{i}\). The angle of incidence determines how the light ray will interact with the surface and the direction in which it will be reflected.
Angle of Reflection: The angle of reflection is the angle between the reflected light ray and the normal. It is denoted by the symbol \(\theta_{r}\). In accordance with the law of reflection, the angle at which light is reflected is equivalent to the angle at which it is incident. This law states that the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal all lie in the same plane.
The Role of Reflection in Visibility:
Reflection plays a fundamental role in making objects visible to us. When light rays reflect off an object and enter our eyes, they form an image that our brain processes, allowing us to perceive the object. The interaction of light with various surfaces, such as smooth or rough, matte or shiny, influences the nature of reflection and how we perceive objects in our environment.
Light, as a fascinating phenomenon, paves the way for our perception of the world. Understanding light rays, the process of reflection, and the concepts of the angle of incidence and angle of reflection provides us with insights into the science behind visibility. As we unravel the mysteries of light, we gain a deeper appreciation for the remarkable properties and behaviors of this essential element of our universe.